KSampler (Advanced)
The KSampler (Advanced) node provides fine-grained and modular control of the denoising process in ComfyUI, letting advanced users customize every aspect of the sampling loop for creative experiments, iterative refinement, and special workflows. It expands on the basic KSampler by enabling partial denoising, noise injection, multi-stage workflows, and beyond.
Overview
KSampler (Advanced) supports advanced use cases such as partial denoising cycles, handover between samplers,
and multi-stage inpainting by enabling you to skip noise addition, control denoising boundaries (start_at_step, end_at_step),
or even return intermediates for further processing. The node is essential for users building workflows that require more than “start-to-end”
diffusion or that need reproducible, highly-customizable image generation.
Visual Example
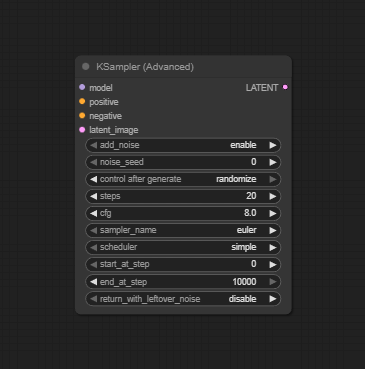
Official Documentation Link
https://blenderneko.github.io/ComfyUI-docs/Core%20Nodes/Sampling/KSampler%20Advanced/
Inputs
| Parameter | Data Type | Input Method | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| model | Object | Model loader node output | — |
| latent_image | Tensor | Node input/connection | — |
| positive | Embedding | Prompt conditioning input | — |
| negative | Embedding | Prompt conditioning input | — |
| steps | Integer | Numeric field/slider | 20 |
| cfg | Float | Numeric field/slider | 7.0 |
| sampler_name | String/Option | Dropdown (e.g., "euler", "dpmpp_2m", etc.) | euler |
| scheduler | String/Option | Dropdown (auto, or specific scheduler) | automatic |
| add_noise | Boolean | Checkbox | True |
| return_with_leftover_noise | Boolean | Checkbox | False |
| seed | Integer | Numeric field | Random |
| start_at_step | Integer | Numeric field | 0 |
| end_at_step | Integer | Numeric field | steps |
Outputs
| Output Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| latent | Tensor | Sampled latent tensor after denoising (partial or full) ready for decoding |
Usage Instructions
Add a KSampler (Advanced) node to your workflow canvas. Connect your model, latent_image, positive,
and negative conditioning nodes as appropriate. Set the desired values for steps, cfg,
sampler_name, and scheduler. Use add_noise to toggle noise addition
(disable for partial denoising or refine cycles). Tune start_at_step and end_at_step
for iterative or partially completed denoising. Enable return_with_leftover_noise if you want intermediary outputs
for progressive workflows. Use the output latent as the basis for further refinement or final decode to image using VAE Decode.
Advanced Usage
Chain several KSampler (Advanced) nodes by handing off leftover noise/tensors for iterative, multi-stage denoising or inpainting. Perform partial denoise + add-and-refine cycles for repairing, upscaling, or region-based edits. Benchmark and experiment using a variety of samplers and schedulers, switching mid-workflow using advanced routing nodes. Pair with custom control nodes or script-based testing nodes for research and ablation studies.
Example JSON for API or Workflow Export
{
"id": "ksampler_adv_1",
"type": "KSamplerAdvanced",
"inputs": {
"model": "@load_diffusion_model_1",
"latent_image": "@emptysd3latentimage_1",
"positive": "@conditioning_positive_1",
"negative": "@conditioning_negative_1",
"steps": 40,
"cfg": 7.0,
"sampler_name": "dpmpp_2m",
"scheduler": "automatic",
"add_noise": true,
"return_with_leftover_noise": false,
"seed": 1337,
"start_at_step": 10,
"end_at_step": 40
}
}Tips
- Only enable
add_noisefor initial denoise cycles; disable for iterative refinements. - Set
start_at_stepandreturn_with_leftover_noisefor multi-stage relaxed or specialized pipelines. - Save seeds and all parameters for reproducibility in collaborative or research settings.
- If you want only partial denoising, set start/end at less than full step range and chain accordingly.
- For speed, reduce steps; for maximal quality, tune cfg/sampler/scheduler combinations.
How It Works (Technical)
KSampler (Advanced) executes a configurable subset of the standard denoising schedule. It may skip noise addition or start/stop mid-way, allowing for nonstandard workflows and partial processing. It supports outputting both the current latent and any leftover noise, making it ideal for progressive, iterative, or experimental workflows where composable pipeline steps are required.
Github Alternatives
- ComfyUI-TripleKSampler – Provides simple, advanced, and alternative KSampler nodes for advanced and chained sampling workflows.
- Efficiency Nodes for ComfyUI – Includes KSampler Adv. (Efficient), supporting live previews, partial denoise, and flexible workflow design.
- KSampler Tester/Loop – Lets you systematically test combinations of sampler parameters in batch and looped workflows, featuring advanced and custom sampler support.
Videcool workflows
The KSampler (Advanced) node is used in the following Videcool workflows:
FAQ
1. How is KSampler (Advanced) different from basic KSampler?
It adds settings for fine control: disables/enables noise addition, sets step start/end, returns partial/noise for advanced chaining.
2. How do I perform multi-stage denoising?
Chain multiple KSampler (Advanced) nodes, adjusting start/end steps and input latent/tensor at each stage.
3. Can I use all the same samplers/schedulers?
Yes; this node exposes and enhances all sampler/scheduler options from core and plug-in extensions.
Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting
Common mistakes include forgetting to disable add_noise for refinement cycles, leading to repeated unnecessary denoising.
Mismatched latent and model inputs can cause errors; always verify correct node chaining. Leaving start/end steps on defaults (0/full)
when partials are desired is problematic; always tune explicitly. Memory overloads on long chains can be addressed by reducing batch,
image size, or cleaning up in multi-stage workflows. Seed management is important—ensure seeds propagate for reproducibility if comparing results across runs.
Conclusion
KSampler (Advanced) is a power-user’s tool for building complex, robust, and fully-customized image generation pipelines in ComfyUI. With detailed step, chain, and noise controls, it is essential for specialized workflows, research, and creative AI experiments.