Load Image (RMBG)
The Load Image (RMBG) node (AILab_LoadImage) loads an image from disk (or a configured directory) into ComfyUI and optionally extracts a mask from one of its color channels, providing an efficient entry point for background‑removal and segmentation workflows.
Overview
Load Image (RMBG) is part of the ComfyUI‑RMBG suite and is tailored for scenarios where an input image and a channel‑derived mask are both needed, such as subject isolation, matting, or pre‑processing for RMBG‑2.0 background‑removal models. It loads the selected image file, can rescale it according to several modes, and extracts a binary or grayscale mask from a chosen channel (alpha, red, green, or blue), also producing an RGB visualization of that mask plus the image dimensions. These outputs connect directly to RMBG, segmentation, compositing, and inpainting nodes in downstream pipelines.
Visual Example
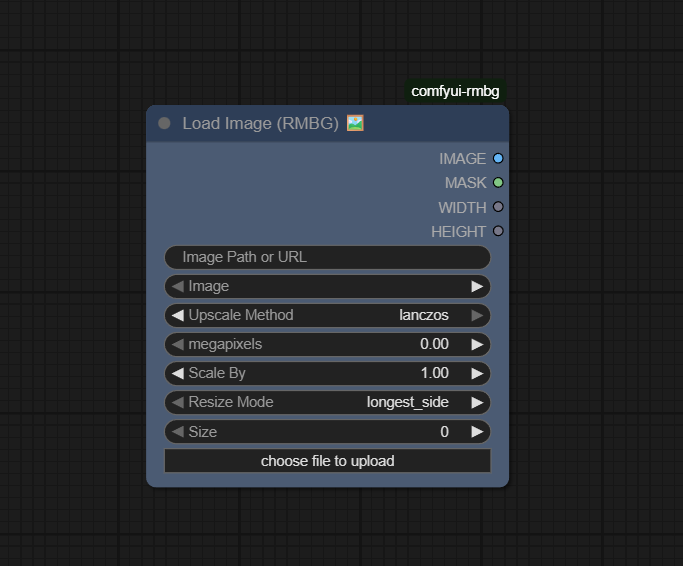
Official Documentation Link
https://comfyai.run/documentation/AILab_LoadImage
https://github.com/1038lab/ComfyUI-RMBG
Inputs
| Parameter | Data Type | Input Method | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| image | STRING | Dropdown / file selector listing available images in the configured directory | First image in list / none selected |
| mask_channel | STRING | Dropdown: alpha, red, green, blue |
alpha |
| scale_by | FLOAT | Numeric field / slider (scale factor applied to both dimensions) | 1.0 |
| resize_mode | STRING | Dropdown: longest_side, shortest_side (and in newer versions width/height modes) |
longest_side |
| size | INT | Numeric field (target size, interpreted according to resize_mode) |
0 (no explicit resizing beyond scale_by) |
Outputs
| Output Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IMAGE | IMAGE | The loaded (and optionally resized/scaled) image tensor used as the main input for processing |
| MASK | MASK | Single‑channel mask tensor extracted from the specified mask_channel (alpha or color channel) |
| MASK_IMAGE | IMAGE | RGB visualization of the mask, useful for previews, overlays, or additional image‑space operations |
| WIDTH | INT | Width in pixels of the loaded (post‑resize) image |
| HEIGHT | INT | Height in pixels of the loaded (post‑resize) image |
Usage Instructions
Select Load Image (RMBG) from the AILab/RMBG category and choose an image filename from the dropdown
list of available files in your configured directory. Pick the mask_channel to indicate where the subject mask resides
(for example alpha for images with transparency or a color channel for chroma‑key–style masks), then adjust scale_by,
resize_mode, and size if you want to normalize resolution for downstream models. Connect IMAGE
and MASK to RMBG, segmentation, or compositing nodes, and optionally use MASK_IMAGE plus
WIDTH/HEIGHT for previews, overlays, or assertions about input size.
Advanced Usage
In advanced background‑removal workflows, you can feed MASK from Load Image (RMBG) directly into RMBG or LayerStyle nodes
to combine channel‑based masks (for example provided by a 3D renderer) with AI‑predicted masks for more controlled composites.
When preparing training or evaluation sets, the node can standardize resolution via resize_mode and size,
ensuring every image/mask pair conforms to the input requirements of downstream networks. For pipelines that mix multiple mask
strategies (alpha, green‑screen, segmentation), chaining multiple Load Image (RMBG) instances or combining their masks with
math/mask‑merge nodes enables complex region selection before final matting or relighting.
Example JSON for API or Workflow Export
{
"id":"ailab_load_image_1",
"type":"AILab_LoadImage",
"inputs":{
"image":"sample_input.png",
"mask_channel":"alpha",
"scale_by":1.0,
"resize_mode":"longest_side",
"size":0
}
}Tips
- Use
mask_channel = alphawhen working with PNGs or formats that already contain a clean transparency mask; this often yields better results than re‑segmenting from RGB. - For green‑screen or chroma‑key footage, experiment with
red,green, orbluechannels to derive a simple thresholdable mask before refining with AI‑based RMBG nodes. - Keep
scale_bynear 1.0 and rely onresize_mode+sizeto adjust resolution uniformly across a dataset, which helps preserve aspect ratio and consistent framing. - Use
MASK_IMAGEin a side‑by‑side viewer or stitched reference panel to quickly inspect mask quality before running heavier background‑removal or compositing pipelines. - Organize your image directory clearly (for example by project or input type) so the
imagedropdown remains easy to navigate in large production setups.
How It Works (Technical)
Load Image (RMBG) reads the selected file from disk, converts it into an internal tensor representation,
and applies optional resizing based on scale_by, resize_mode, and size,
typically preserving aspect ratio as configured. It then selects the requested mask_channel: for
alpha, it extracts the alpha plane; for red, green, or blue,
it slices the corresponding channel from the RGB data and normalizes it into a mask tensor. A separate MASK_IMAGE
is generated by mapping the mask into an RGB visualization (for example grayscale), while WIDTH and
HEIGHT are computed from the final image dimensions. All tensors are returned in ComfyUI’s IMAGE and
MASK formats so they can be consumed directly by RMBG and segmentation nodes.
Github alternatives
- ComfyUI-RMBG – the full RMBG suite that includes Load Image variants, RMBG background‑removal, segmentation, and advanced compositing nodes built around RMBG‑2.0 and related models.
- ComfyUI-Inpaint-CropAndStitch – a toolkit for cropping, stitching, and inpainting that complements RMBG pipelines when you need spatial transforms or multi‑region edits around masked subjects.
- top-100-comfyui – an automatically updated index of popular ComfyUI repositories, helpful for discovering alternative loaders, mask generators, and background‑removal extensions beyond RMBG.
FAQ
1. Do I need RMBG models installed to use Load Image (RMBG)?
No, Load Image (RMBG) itself only loads images and extracts masks from channels; however, it is typically used together with
RMBG or segmentation models that consume those outputs.
2. What is the difference between MASK and MASK_IMAGE?
MASK is a single‑channel
tensor intended for processing (matting, compositing, model inputs), while MASK_IMAGE is an RGB visualization
of the mask that is easier to preview and overlay in image‑space workflows.
3. How should I choose resize settings for best results?
Use resize_mode = longest_side or shortest_side with a size
that matches your downstream model’s expected resolution, and keep scale_by at 1.0 unless you
need an extra global scale adjustment.
Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting
A common pitfall is selecting a mask_channel that does not actually contain meaningful mask data
(for example alpha on a JPEG or a color channel with low contrast), resulting in nearly empty or noisy masks;
in such cases, inspect MASK_IMAGE and adjust the channel choice or your source images. Another frequent
issue is mismatched resizing relative to downstream models: overly aggressive scaling or inappropriate resize_mode
can distort subjects or reduce segmentation accuracy, so align your size settings with the requirements of RMBG or
segmentation networks. If the node fails to list images in the dropdown, verify that the configured directory exists,
that the file formats are supported (PNG, JPG, etc.), and that paths match your ComfyUI‑RMBG installation; missing or
mis‑installed RMBG packages can also prevent the node from registering correctly.
Conclusion
Load Image (RMBG) is a powerful entry node for background‑aware workflows in ComfyUI, combining robust image loading, flexible resizing, and channel‑based mask extraction to streamline background removal, segmentation, and advanced compositing pipelines for both creative and production use.