Clip Text Encode (Positive Prompt)
This page documents the typical ComfyUI node format used to encode positive prompts with the CLIP text encoder (often shown in the UI as CLIP Text Encode (Prompt)). It includes the node's purpose, common fields seen in saved workflows / API exports, copyable example JSON, and practical tips for composing positive prompts.
Overview
The CLIP Text Encode (Positive Prompt) node in ComfyUI is used to encode a text prompt using a CLIP model into an embedding that can guide the diffusion model in generating images. It transforms human-readable text into a numerical representation suitable for conditioning in image generation workflows. This node is typically used for positive prompts, which describe the desired elements in the generated image, but the underlying functionality is similar to the general CLIP Text Encode node. The distinction between positive and negative prompts is often handled by using separate instances of the node and connecting them accordingly in the workflow.
Visual Example
Below is a screenshot of the node in the ComfyUI interface:
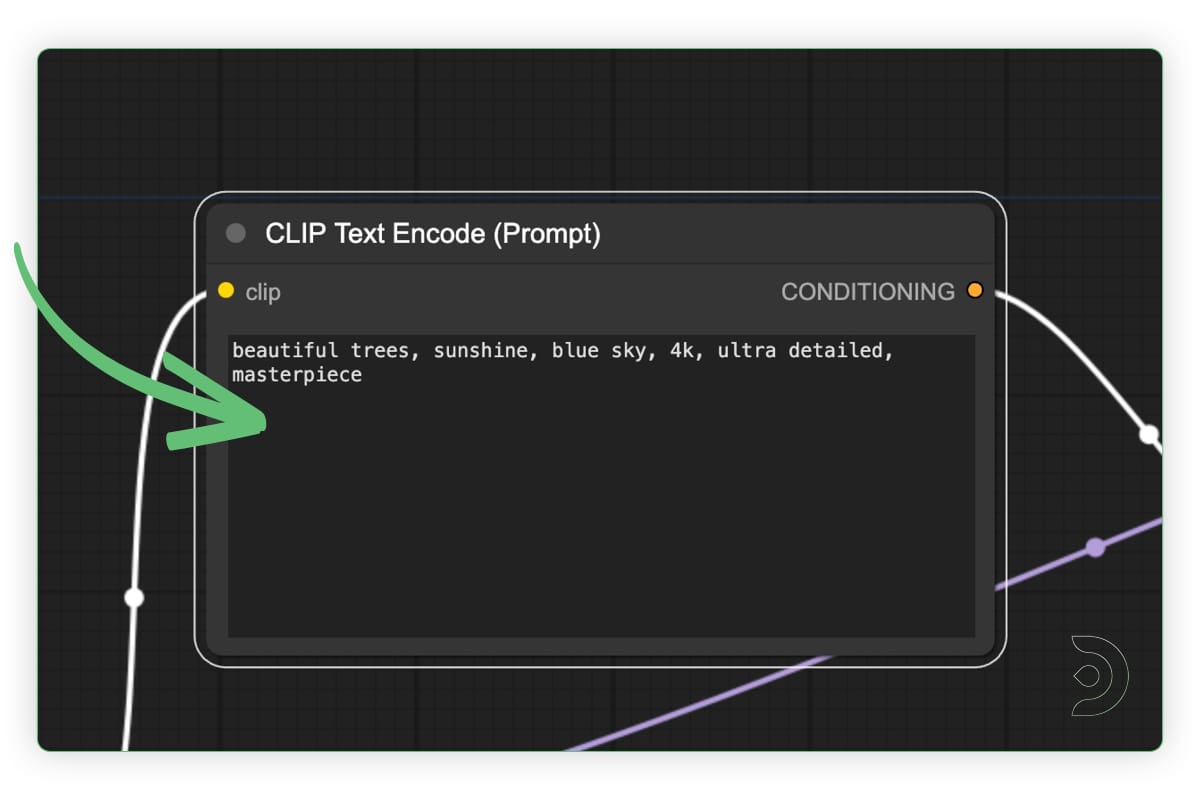
Official documentation
https://docs.comfy.org/built-in-nodes/ClipTextEncode
Inputs
The primary input parameter is the 'text' input, which supports basic prompting techniques such as comma-separated keywords. It does not natively support complex weighting syntax like ((text:1.4)). Embeddings can be included using the syntax embedding:ModelName.
| Parameter | Data Type | Input Method | Default |
| clip | Clip | Model Selection | None |
| text | STRING | Text Input | Empty |
Outputs
| Output Name | Data Type | Description |
| conditioning | CONDITIONING | These are the translated “painting instructions” containing detailed creative guidance that the AI model can understand. These instructions tell the AI model how to create an image matching your description. |
Usage
In a standard workflow, connect the CLIP output from a Load Checkpoint node to this node's clip input. Enter a descriptive positive prompt in the text field. Connect the conditioning output to the positive prompt input of a sampler node like KSampler.
For advanced usage, combine with nodes like CLIP Set Last Layer for layer truncation or Conditioning Combine for multiple conditionings.
Examples
- Basic positive prompt: "a serene mountain landscape, vibrant colors, detailed foreground"
- With embedding: "beautiful portrait, embedding:EasyPositive, high resolution"
Tips
- Use clear descriptive nouns and adjectives up-front:
"golden retriever, smiling, studio light". - Use parentheses or weight syntax if your encoder/parser supports it:
(feature:1.2)or suffix weights like:1.2— behaviour depends on the node/extension you use. - Break complex prompts into multiple nodes when you need per-prompt weights or different tokenization strategies (some custom nodes implement multi‑prompt handling).
- Remember: positive prompts bias the generation toward the included concepts — be concise when you want strong guidance.
How It Works (Under the Hood)
The CLIP Text Encode (Positive Prompt) node converts human-readable text into a vector representation that a diffusion model can understand. Internally, CLIP tokenizes your prompt into smaller text units called tokens, looks them up in its vocabulary, and processes them through transformer layers to produce an embedding. This embedding is then passed into the sampler as conditioning, influencing how the model forms shapes, styles, and concepts during generation. Different model families (SD1.5, SDXL, Flux, etc.) may use different CLIP variants, which affects token limits, accuracy, and how strongly prompts influence results.
JSON node
The snippet below shows a minimal, copyable example of how a CLIP text encode node frequently appears inside a ComfyUI workflow JSON (API-style). This is intentionally generic - some exported files add more metadata or different keys depending on ComfyUI version and extensions.
{
"nodes": [
{
"id": "node_clip_1",
"type": "CLIPTextEncode",
"x": 160,
"y": 120,
"properties": {"text": "A cinematic portrait of a fox in a snowy forest, dramatic lighting, 35mm"}
}
],
"connections": []
}Advanced JSON
Multiple positive prompts (conceptual example)
{
"nodes": [
{
"id": "clip_pos_a",
"type": "CLIPTextEncode",
"properties": {"text":"golden retriever:1.5"}
},
{
"id": "clip_pos_b",
"type": "CLIPTextEncode",
"properties": {"text":"studio portrait, high detail"}
}
],
"connections": [
{"from":"clip_pos_a","to":"ConditioningMixer","slot":0},
{"from":"clip_pos_b","to":"ConditioningMixer","slot":1}
]
}Above, two CLIP nodes encode different positive prompts and feed a hypothetical ConditioningMixer that combines their embeddings. Actual node names and slot numbers depend on the target workflow and installed extensions.
Github alternatives
CLIP Text Encode++:
https://github.com/shiimizu/ComfyUI_smZNodes
Advanced CLIP Text Encode:
https://github.com/BlenderNeko/ComfyUI_ADV_CLIP_emb
Styled CLIP Text Encode:
https://github.com/microbote/ComfyUI-StyledCLIPTextEncode
Compatibility notes & tips
ComfyUI has multiple CLIP/encoder variants for different model families (vanilla CLIP, SDXL-aware encoders, and community extensions). Check the node name ( some versions append SDXL or extension names). Saved JSON from different ComfyUI versions may change keys. If you parse or modify workflows programmatically, prefer the API-format exports where available. If you rely on prompt-weighting syntax, test on a small workflow first. Different nodes/extensions implement weights differently.Videcool workflows
The Clip Text Encode (Positive Prompt) node is used in the following Videcool workflows:
FAQ
1. What does the CLIP Text Encode (Positive Prompt) node do?
It converts your written prompt into a numerical embedding using a CLIP model.
This embedding is then used by diffusion samplers to guide image generation toward
the concepts you describe.
2. Do I need a specific CLIP model for this node?
Yes. The node requires a CLIP model that matches the checkpoint you loaded.
Typically, you connect the CLIP output from a Load Checkpoint node directly
into the node’s clip input.
3. Can I use weighting or advanced prompt syntax?
The built-in node supports simple text input but does not natively
process complex weighting like ((prompt:1.4)). Some extensions add this
functionality, so behavior may vary depending on your installed nodes.
4. How do I include embeddings in my prompt?
You can reference an embedding using the syntax embedding:EmbeddingName
inside your prompt. The exact name should match a loaded embedding available in your
ComfyUI environment.
5. Why would I use multiple CLIP Text Encode nodes?
Multiple nodes allow you to encode separate concepts with individual weights or
combine them using mixers such as Conditioning Combine or custom extension
nodes. This enables more advanced prompting and finer control over conditioning
strength.
Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting
Many issues with prompt behavior stem from incorrect node connections or assumptions about how CLIP handles text. If your prompt appears to have no effect, verify that the CLIP model from the Load Checkpoint node is correctly connected. If prompt weights aren't working, ensure you're using a node or extension that supports weighting syntax. When positive and negative prompts produce unexpected interactions, double-check that each conditioning output is routed to the correct input on the sampler node.
Conclusion
The CLIP Text Encode (Positive Prompt) node is a foundational component in ComfyUI workflows, converting human-written prompts into the conditioning vectors that guide image generation. By understanding its inputs, outputs, and behavior across different model families and extensions, you can craft more deliberate and effective prompts. Whether you are building simple workflows or experimenting with multi-prompt setups and advanced conditioning techniques, mastering this node ensures clearer control over how your creative intentions translate into generated imagery.