Remove Background (RMBG)
The Remove Background (RMBG) node provides advanced AI‑based background removal and segmentation in ComfyUI, generating clean foreground cutouts and masks from input images using models like RMBG‑1.4 and RMBG‑2.0.
Overview
Remove Background (RMBG) analyzes an input image to separate foreground subjects (people, products, clothing, etc.) from their backgrounds, outputting both a background‑removed image and the underlying mask. It supports multiple background‑removal models and configuration options so you can choose between transparent outputs, solid‑color backgrounds, or just masks for further processing. In typical workflows it sits after an image loader (such as Load Image or Load Image (RMBG)) and before compositing, LayerStyle, or save nodes.
Visual Example
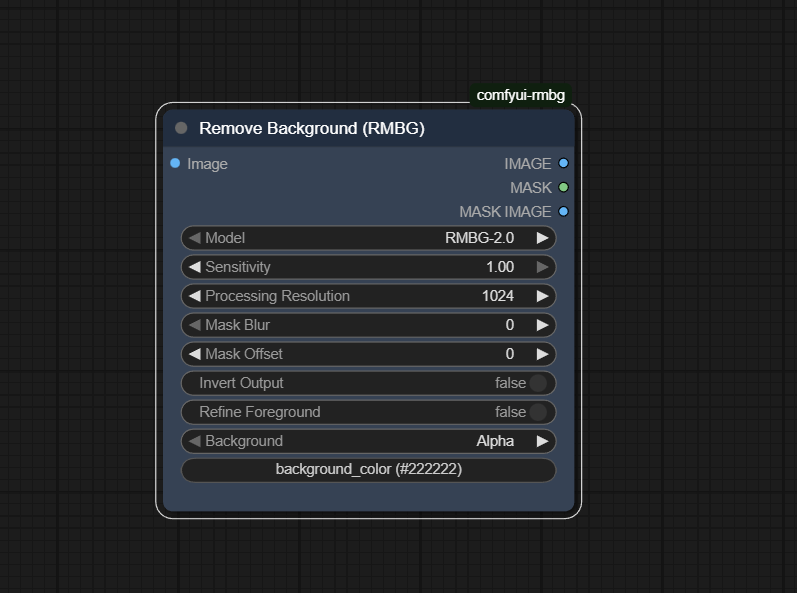
Official Documentation Link
https://comfyai.run/documentation/Image Remove Background (RMBG) [LP]
https://comfyai.run/documentation/RMBG
Inputs
| Parameter | Description | Input Method | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| image | Image (or batch of images) from which the background will be removed. | Connection from Load Image, Load Image (RMBG), or any IMAGE‑producing node | — (required) |
| model | Background‑removal model to use, such as RMBG-1.4, RMBG-2.0, INSPYRENET, or BEN2, depending on installed RMBG version. |
Dropdown list of available RMBG / segmentation models | RMBG-2.0 or plugin default |
| output_mode | Controls how the result is handled (for example hide/preview/save in some UIs, or whether to output only mask vs full image). | Dropdown (for Easy‑Use variants) or boolean/toggles on core RMBG node | Preview / full image with transparency |
| transparency | If true, output has transparent background; if false, background is replaced with a solid color. | Checkbox / boolean toggle | true |
| background_color | Solid background color when transparency is disabled; often wired from Color Input (RMBG). | COLOR input (hex string or RGB, depending on implementation) | None / transparent |
| alpha_threshold | Threshold used when alpha‑matting is enabled, controlling how aggressively background is removed. | Numeric field, 0–255 | 10 |
| alpha_erosion | Erosion size applied to the alpha matte to shrink or tighten the foreground edges. | Integer slider | 10 |
| post_process | Enables extra refinement filters after initial segmentation to clean up edges and residual noise. | Checkbox / boolean toggle | false |
| only_mask | If true, node outputs just a binary mask instead of a composited foreground image. | Checkbox / boolean toggle | false |
Outputs
| Output Name | Description |
|---|---|
| IMAGE | The processed image with background removed or replaced (transparent or solid color), suitable for compositing, product shots, or further editing. |
| MASK | The foreground/background mask used by the algorithm, where foreground is typically white and background black, useful for refinements or external composites. |
Usage Instructions
In a typical workflow, start with Load Image or Load Image (RMBG) to bring an image into ComfyUI, then connect its
IMAGE output to the image input of Remove Background (RMBG). Choose a model
that suits your quality and speed needs (for example RMBG-2.0 for high quality or lighter models for speed),
and decide whether you want a transparent result (transparency = true) or a solid background, optionally
set via background_color. Adjust refinement parameters like alpha_threshold and
alpha_erosion only if edges look imperfect, then connect IMAGE to a preview or
save node; optionally, use MASK with LayerStyle or compositing nodes for more advanced control.
Advanced Usage
Advanced pipelines often run several Remove Background or easy imageRemBg variants in parallel with different models (RMBG‑1.4, RMBG‑2.0, INSPYRENET, BEN2) and then select the best mask or composite result per image, as seen in multi‑model comparison workflows. When combined with Color Input (RMBG) and LayerStyle, RMBG outputs can be quickly placed onto brand‑colored backdrops, blurred photographic plates, or gradient cards for high‑end product visuals. For video or batch processing, place Remove Background (RMBG) inside a loop or use batch‑capable variants so the same model and parameter set is applied consistently across many frames or assets; this is particularly useful for fashion/identity videos and e‑commerce catalogs.
Example JSON for API or Workflow Export
{
"id":"rmbg_1",
"type":"RMBG",
"inputs":{
"image":"@ailab_load_image_1:IMAGE",
"model":"RMBG-2.0",
"output_mode":"Preview",
"transparency":true,
"background_color":"#00000000",
"alpha_threshold":10,
"alpha_erosion":10,
"post_process":false,
"only_mask":false
}
}
Tips
- Start with the recommended model for your RMBG version (typically
RMBG-2.0) and only switch to alternatives like INSPYRENET or BEN2 if edge behavior or hair detail is unsatisfactory. - Keep
transparencyenabled while checking mask quality; switch to a solidbackground_coloronly after you are satisfied with edges and holes. - Use
only_maskwhen you want to drive custom composites or LayerStyle pipelines, as it lets you separate mask generation from final rendering. - If processing many large images, consider lowering resolution up front or using batch‑oriented workflows to keep VRAM usage reasonable.
- Save both the cut‑out image and mask when producing assets for downstream tools (Photoshop, web apps) so teammates can refine edges without re‑running RMBG.
How It Works (Technical)
Remove Background (RMBG) feeds the input image through a background‑removal network such as RMBG‑1.4 or RMBG‑2.0,
which predicts an alpha matte or segmentation mask representing foreground likelihood per pixel. This raw mask is optionally refined using
alpha_threshold, alpha_erosion, and post‑processing to clean edges and remove noise, then used to composite
the original image against either transparency or a user‑specified background_color. The mask tensor is returned alongside
the composited output so it can be reused in subsequent nodes, and different models can be swapped without altering the surrounding
workflow because the interface (image in, cut‑out + mask out) stays consistent.
Github alternatives
- ComfyUI-RMBG – main RMBG extension providing the Remove Background node, model loaders, and related segmentation tools, with support for RMBG‑2.0 and other backends.
- rembg-comfyui-node – an alternative background‑removal node that wraps the
rembglibrary (U2Net and related models), offering a simpler but flexible remove‑background operation. - Awesome ComfyUI custom nodes – curated list that includes Easy‑Use background‑removal nodes (for example
easy imageRemBg) and other segmentation utilities built on RMBG and Inspyrenet.
FAQ
1. Which RMBG model should I pick for best quality?
RMBG‑2.0 is generally recommended for high‑quality cut‑outs and improved edge handling over RMBG‑1.4, though models like INSPYRENET or
BEN2 may perform better on some scenes; testing a few models on your content is the best way to decide.
2. Can this node output just a mask instead of a cut‑out image?
Yes, by enabling options like only_mask (or the equivalent mode in Easy‑Use variants), the node can return a binary
or grayscale mask that you can use for custom compositing, inpainting, or analysis.
3. How does this differ from Image Rembg / Easy imageRemBg nodes?
Remove Background (RMBG) is the dedicated RMBG extension node with direct access to RMBG‑series models and advanced options, while
Easy imageRemBg nodes wrap multiple background‑removal backends behind a simplified interface; both perform similar tasks but expose
different parameter sets and model choices.
Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting
A frequent issue is installing RMBG models incorrectly or not selecting a valid model in the node, which leads to errors or
very poor masks; always confirm that RMBG‑1.4 or RMBG‑2.0 weights are placed in the documented folders and that the chosen
model name matches what is installed. Another common pitfall is running RMBG directly on very high‑resolution images without
resizing, causing slow inference or out‑of‑memory problems—downscale large inputs or use batch approaches for big sets.
If edges look jagged or halos appear, tweak alpha_threshold, enable post_process, or follow with
light blur/feathering in LayerStyle nodes; complex backgrounds with low contrast may still require some manual cleanup.
Finally, if exported images lose transparency, verify that your save node is writing PNG (or another alpha‑aware format)
and that no intermediate node flattens the alpha channel.
Conclusion
Remove Background (RMBG) is a cornerstone of background‑removal workflows in ComfyUI, combining modern segmentation models, flexible output options, and mask access into a single node that significantly streamlines creating clean cut‑outs for design, e‑commerce, video, and advanced compositing tasks.